The year 2024 will be marked as a significant milestone in the political journey of India as the nation geared up for its national elections. With fervor and anticipation, citizens across the country engaged in the democratic process, casting their votes to determine the course of the nation’s future. The 2024 elections are not merely about selecting representatives; they were a reflection of India’s evolving socio-political dynamics, presenting a tableau of diverse aspirations, ideologies, and challenges.
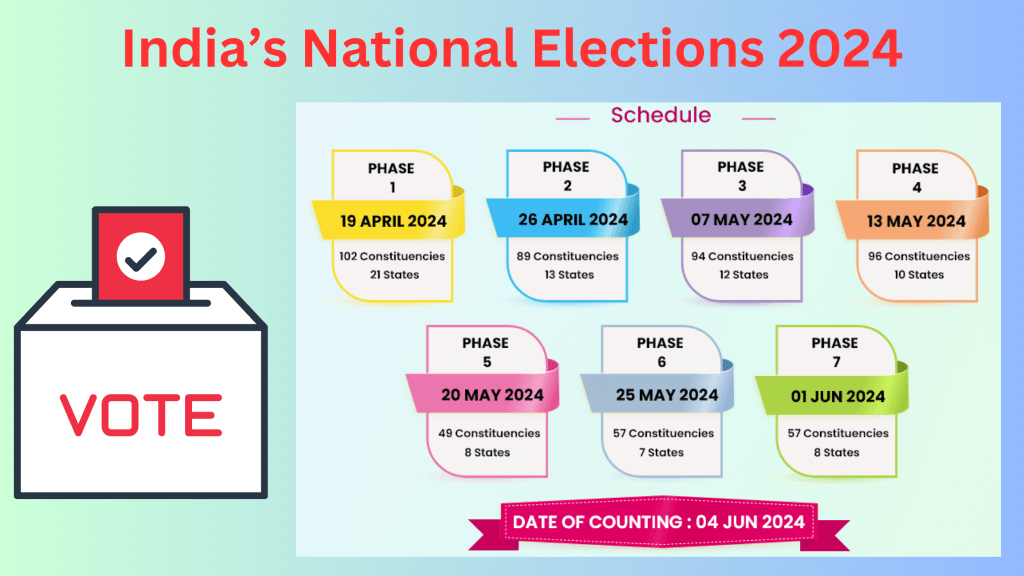
State Wise Polling Dates
The electoral process in India, a vibrant democracy, unfolds across its vast expanse in a phased manner to ensure a smooth and efficient conduct of elections. State-wise polling dates are meticulously planned and announced by the Election Commission of India, taking into account various factors such as geographical spread, security concerns, and logistical feasibility.
These polling dates serve as the cornerstone of the democratic exercise, determining when citizens in different states exercise their right to vote and shape the political landscape. From the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas to the sun-kissed shores of the Indian Ocean, each state holds its pivotal moment in the electoral calendar, contributing to the diverse tapestry of Indian democracy.
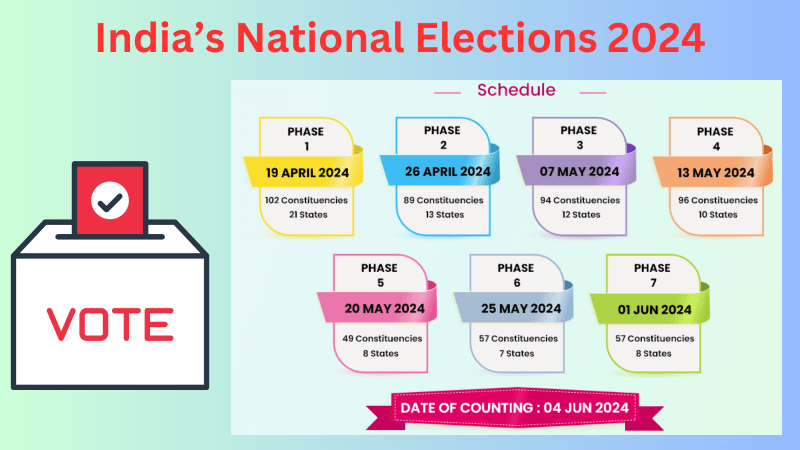
These dates not only signify the culmination of months of campaigning and political discourse but also mark the beginning of a journey towards determining the collective will of the people. As polling unfolds across the nation, it underscores the essence of democracy – the power vested in the hands of the electorate to choose their representatives and chart the course of the nation’s future. The phase wise dates are given below.
Phase 1 Polling Date – 19.04.2024
Click here to see the states with Constituencies going to poll on the 19th April 2024
Phase 2 Polling Date – 19.04.2024
Click here to see the states with Constituencies going to poll on the 26th April 2024
Phase 3 Polling Date – 07.05.2024
Click here to see the states with Constituencies going to poll on the 07th May 2024
Phase 4 Polling Date – 13.05.2024
Click here to see the states with Constituencies going to poll on the 13th May 2024
Political Landscape:
In the lead-up to the elections, the political landscape witnessed a multitude of narratives, alliances, and debates. Traditional political stalwarts vied for supremacy while emerging parties sought to challenge the status quo. The contours of Indian politics were reshaped by issues ranging from economic revival and social justice to national security and environmental sustainability.
Participating Players:
At the forefront were the incumbent parties, buoyed by their past performance and promising continuity. Opposition parties, on the other hand, rallied behind alternative visions, critiquing the government’s policies and promising transformative change. Additionally, regional parties wielded significant influence, especially in states with distinct socio-cultural identities, playing pivotal roles in shaping the national narrative.
Key Issues:
The electoral discourse revolved around a myriad of pressing issues that resonated with the electorate. Economic revival, exacerbated by the global pandemic, stood out as a central concern, with unemployment, inflation, and economic inequality dominating discussions. Social justice and inclusivity emerged as focal points, with debates on caste-based discrimination, gender equality, and minority rights gaining prominence.
National security remained a cornerstone issue, given the geopolitical tensions and internal security challenges facing the country. Environmental sustainability also commanded attention, with climate change impacts and conservation efforts finding a place in political agendas.
Technological Influence:
The 2024 elections are going to witness an unprecedented infusion of technology into the electoral process. Digital campaigning, social media outreach, and data analytics played a crucial role in shaping voter opinions and mobilizing support. Candidates leveraged online platforms to connect with voters, disseminate their agendas, and counter opposition narratives. However, concerns regarding misinformation, data privacy, and algorithmic bias underscored the challenges posed by the digital age to democratic norms.
Youth Engagement:
The youth will emerge as a significant demographic in the electoral landscape, with their aspirations and grievances driving political discourse. Empowered by social media and digital connectivity, young voters demanded accountability, transparency, and progressive policies from political parties. Issues such as education reform, employment generation, and environmental sustainability resonated strongly with the youth, highlighting their role as catalysts for change.
Regional Dynamics:
India’s federal structure plays a crucial role in the electoral calculus, with regional dynamics often shaping the national outcome. Regional parties, rooted in local identities and aspirations, wielded considerable influence in their respective states, challenging the dominance of national parties. Coalition politics, therefore, remained a recurring theme, with post-election alliances crucial in determining the formation of the central government.
Deciphering the Essence of Lok Sabha Elections
Lok Sabha elections, often termed as the festival of democracy in India, hold a significant place in the country’s political landscape. These elections not only determine the composition of the lower house of the Indian Parliament but also reflect the collective will of over a billion people. As the largest democratic exercise globally, Lok Sabha elections showcase the diversity, complexity, and vibrancy of Indian democracy. Let’s delve into the essence of Lok Sabha elections and unravel their multifaceted significance.
Historical Context:
The journey of Lok Sabha elections traces back to the adoption of the Indian Constitution in 1950. Since then, India has witnessed regular and free elections to choose its representatives at the national level. The first general elections held in 1951-52 marked a historic moment, where millions of Indians exercised their franchise, laying the foundation of democratic governance in independent India.
Democratic Principles at Play:
Lok Sabha elections epitomize the democratic principles of equality, inclusivity, and representation. Every eligible citizen above the age of 18 has the right to vote, irrespective of caste, creed, religion, gender, or socio-economic status. This egalitarian ethos underscores the essence of Indian democracy, empowering individuals to participate in the decision-making process and shape the nation’s destiny.
Political Pluralism and Diversity:
India’s vast geographical expanse and diverse socio-cultural fabric find expression in Lok Sabha elections. With 543 constituencies spread across the country, each representing a unique demographic, linguistic, and cultural milieu, these elections reflect the rich tapestry of Indian society. Political parties vie for support by articulating diverse ideologies, catering to the varied aspirations of the electorate.
Role of Political Parties:
Political parties play a pivotal role in shaping the electoral landscape of India. From national parties with pan-Indian influence to regional parties championing local issues, the electoral arena is characterized by a multitude of political actors. Manifestos, campaigns, and rallies serve as platforms for parties to articulate their vision, policies, and promises, seeking the mandate of the people.
Election Machinery and Processes:
The Election Commission of India (ECI) oversees the conduct of Lok Sabha elections, ensuring free, fair, and transparent polls. From voter registration to candidate nomination, polling, and counting, the ECI orchestrates the entire electoral process with meticulous precision. Advanced technological interventions, including Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) and Voter Verified Paper Audit Trails (VVPATs), have enhanced the efficiency and credibility of elections.
Voter Participation and Engagement:
Lok Sabha elections witness robust voter participation, underscoring the democratic fervor among the electorate. Political awareness campaigns, voter education initiatives, and media outreach endeavors strive to enhance voter turnout and engagement. Citizens exercise their electoral rights judiciously, mindful of the profound impact their vote wields in shaping the nation’s governance and policies.
Challenges and Imperatives:
Despite the democratic fervor surrounding Lok Sabha elections, certain challenges persist. Electoral malpractices, money power, identity politics, and polarization pose threats to the sanctity of the electoral process. Strengthening democratic institutions, ensuring electoral integrity, and fostering political discourse based on issues rather than personalities are imperative to fortify India’s democratic edifice.
Conclusion:
Lok Sabha elections embody the essence of Indian democracy, serving as a beacon of hope, empowerment, and accountability. Beyond the political spectacle, they signify the collective aspirations and ideals of a diverse nation marching towards progress and prosperity. As India continues its democratic journey, Lok Sabha elections remain a testament to the resilience and vitality of the world’s largest democracy.