As Indian companies increasingly flock to the United Arab Emirates (UAE), a unique economic dynamic is unfolding. This is not just about trade but also about navigating the complexities of Indian taxation. With a growing diaspora and increasing trade links, Indians are finding the UAE not only a strategic business center but also a haven from India’s complicated tax structure. This article explores the reasons for this trend and examines the implications for individuals and businesses and the evolving financial relationship between India and the UAE.
The UAE Attraction
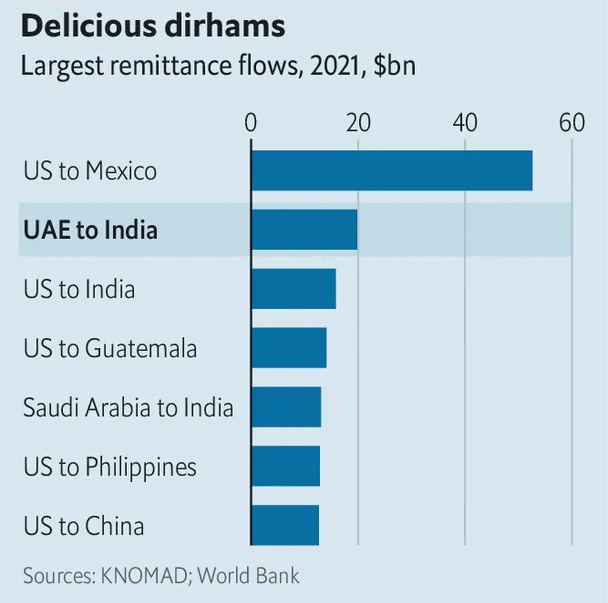
The Meena Bazaar in Dubai, once a symbol of Indian culture, is now a living reflection of a burgeoning economic partnership. With 83,000 Indian-owned companies in the UAE, the influence of the diaspora is clearly noticeable. Indians, who make up 3.5 million of the population, play a central role in the UAE’s thriving economy. These expats sent a total of 20 billion dollars home in 2021, a sum exceeded only by remittances from America to Mexico (see chart). Also, they contribute to thriving Arabic online casinos and sports betting, which are aggregated on A7laBet with a huge welcome bonus, a great no deposit bonus, a free spins bonus, or other bonuses. This influx is driven not only by business opportunities but also by the lure of a simpler tax landscape that attracts both expatriates and investors seeking a break from India’s complicated tax laws.
Tax Comparisons
India’s tax situation, characterized by high personal and corporate taxes, has prompted many to explore the tax haven of the UAE. The fact that there are no personal taxes in the UAE and corporate taxes are manageable is in stark contrast to India’s complicated tax laws. For individuals looking to invest or reside abroad, the UAE’s tax advantages are a compelling argument, which has led to an increase in real estate investment, particularly in Dubai. This trend is further reinforced by the peculiarities of India’s tax laws, which encourage real estate investment for those looking to take their money abroad.
Legal Framework
In addition to taxes, legal differences are also contributing to India’s growing interest in the UAE. The UAE, which operates under Islamic law, has modern commercial courts and supports religious pluralism. In contrast, the Indian legal system struggles with overburdened courts and strict enforcement of certain laws. The UAE’s legal environment not only encourages business growth but also provides a more cosmopolitan backdrop that attracts Indian investors seeking a favorable legal framework for their ventures.
Financial Capital Evolution
The United Arab Emirates is emerging as a financial capital for India, with significant investment flowing in from Emirati sovereign wealth funds and private equity firms. From large banks to start-ups, Indian companies are benefiting from this financial influx, making the UAE an important source of capital. However, this development is facing obstacles, including the UAE’s inclusion on the Financial Action Task Force’s “grey list”, raising concerns about the transfer of funds and prompting some Indians to seek alternative avenues for foreign investment.
Conclusion
In the evolving Indian economic and fiscal landscape, the UAE is a beacon of opportunity. The symbiotic relationship between India and the UAE continues to deepen despite persistent challenges. Indians, lured by the promise of a simplified tax regime and a robust business environment, are reshaping the narrative of economic relations. As the UAE emerges as a financial hub for India, it is critical for those venturing into this dynamic partnership to navigate both the legal nuances and potential obstacles.