The Goods and Service Tax system completes more than 4 years in India on 12.05.2022. The GST was implemented on 01.07.2017 throughout the nation. Thus, there has been a reduction in taxes on various types of goods and services since its implementation. Also, the return filing and registration process have been simplified. On the other hand, over a period of time, the system is able to reveal fake businesses. Thus, it helped to increase the tax base and the overall revenue over the period of time.
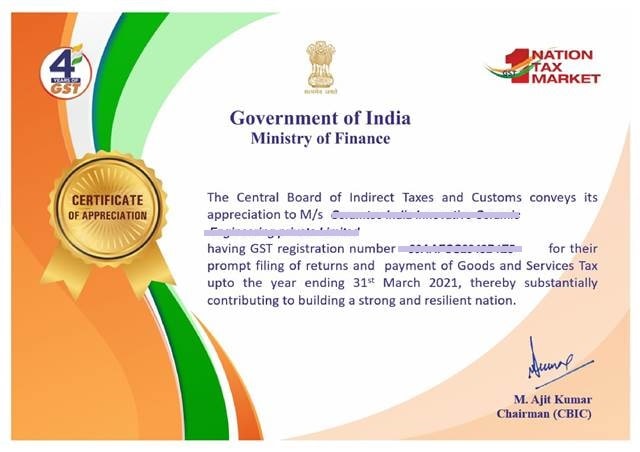
Further, on the eve of the completion of 4 years of GST, the government has honored the taxpayers by issuing a Certificate of appreciation. Thus, the department has identified 54,439 taxpayers for issuing these certificates of appreciation, who filed their GST returns and paid the taxes within the timeframe. The certificate is being sent through email. The taxpayer can download, print, and display these certificates. Below is a screenshot of the certificate of appreciation.
The Finance Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that enhanced revenue collection in recent months should now be the “New Normal”. Similarly, the Prime Minister of India tweeted saying “GST has been a milestone in the economic landscape of India. It has decreased the number of taxes, compliance burden & overall tax burden on a common man while significantly increasing transparency, compliance, and overall collection. #4YearsofGST”.
GST Completes 2 years
30.06.2019: GST leads to Formalization of Economy: A Historic tax reform, the Goods and Service Tax (GST), has resulted in the formalization of the economy, and consequently information flow would eventually augment not only the Indirect Tax collections but also Direct Tax collections.
In the past, the Centre had small data on small manufacturers and consumption because the Central excise was imposed only at the manufacturing stage while the States had very little data on the activities of local firms outside their borders.

Under the GST, there will be now the seamless flow of availability of a common set of data to both the Centre and the States making Direct and Indirect Tax collections more effective.
The introduction of GST in India, a common Indirect Tax for both the States as well as the Central Government with its end to end digitization of all processes, is the biggest reform measure that is already creating more jobs in the formal sector and eliminating transactions that are not recorded earlier in the books of accounts and thus, were outside the tax net so far.
Goods and service tax is designed to bring about better tax compliance and transparency in t
A number of procedural changes have also been made since the roll-out of GST on 1st July 2017 in order to simplify the processes. Further, steps are also being undertaken for further simplification in order to facilitate the taxpayers and to extend benefits to the customers.
Widening of the additional Tax base
There are early signs of tax base expansion. Between June and July 2017, 6.6 lakh new agents, previously outside the tax net, sought Goods and Service Tax registration. This is expected to rise consistently as the incentives for formalization increase.
The entire Textile chain is now brought under the goods and service tax net. Further, a segment of land and real estate transactions has also been brought into Goods and Service tax net “works contracts”, referring to housing that is being built.
This in turn would allow for greater transparency and formalization of cement, steel, and other sales which earlier tended to be outside the GST tax net. The formalization will occur because the builder will need documentation of these input purchases to claim the input tax credit.
GST History in India
GST was rolled out in India on 01.07.2017. It is now 2 years passed since its implementation and the government thinks everything is on the right track. This GST article will help you to understand, where we stand after two years of its implementation. Let us see the history of the E waybill.
E way bill was implemented throughout the country for the Interstate movement of goods from 01.04.2018. Further e way bill for Intra-state movement of goods is also implemented in a phase to phase manner in all states. Below you can see the number of e-way bills generated by taxpayers/transporters.
Summary of GST Details as on 30.6.2019
The total GST registration that took place on the GST portal from July 2017 to June 2019 is 1,22,58,569. In the month of July 2017, the registration taken was 38,51,211.
Developments during the GST journey since 2017
Subsuming Various taxes
It was a new experience of subsuming 17 various types of taxes under Goods and Service Tax. Thus, Pre – GST, Trade & Industry had to undergo compliance’s under Central Excise, Service Tax, and VAT. It involved doing business in multiple states, adhering to different VAT laws, complying through different portals, and answering to different authorities.
All that has been combined into a single robust online system. However, Starting up has become simple with one-stop online registration for wanting to do business anywhere in the country.
State borders
The State borders’ glitches and delays have come down significantly. Due to different VAT laws in different states, inter-state transactions were a pain for Trade and Industry.
CST charged on inter-state transactions were an additional cost with no input credit available and thousands of productive hours were wasted at state border crossings. The cost and time of doing inter-state transactions have come down significantly after the implementation of E way bill.
Rate Rationalisation
Major changes in the GST Tax rates of various items whereby 28% items pulled to 18%, 18% items pulled to 12% & 12% items pulled to 5%. Further various essential goods were made tax-free. Most goods are unbranded and manufactured by MSMEs.
The reduction in almost all the cases has been from the higher to the immediately lower tax slab (whether from 12% to 5% or 18% to 12%) and involves indigenously processed foods, man-made textile yarn, stationery, and other job-work items.
GST Return filing
The original concept of four Tax returns in a month (GSTR 3B, GSTR 1, GSTR 2 & GSTR 3) was gradually curtailed to two tax returns viz: GSTR 3B & GSTR 1.
Further the Govt. extended GST Returns due dates for filing tax returns as and when felt necessary. Quarterly Returns were also prescribed for small taxpayers. Reduction in the late fee payable for delay in filing tax returns from Rs 200/- per day to Rs 50/-per day /Rs 20/- per day.
For the Trade and Industry whose turnover was turnover below five crores, a quarterly return filling system is proposed. This will benefit 93% of the taxpayers, reduce their compliance burden and increase the ease of doing business.
Exports & Refunds
Exports are made possible on the basis of Bond/LUT and without the payment of IGST tax. A major package for exporters/merchant exporters has been announced after discussions with various Export Promotion Councils & organizations like FIEO, APEC, GJEPC, EEPC, Handicraft EPC, etc. Refund Fortnights were conducted from 15th March to 31st March 2018, 31st May to 14th June 2018, and 16th July to 30th July 2018.
GST Law Amendment Act, 2018
In its 28th meeting of the GST Council held in New Delhi on 21.07.2018, the GST Council recommended certain amendments to the CGST Act, IGST Act, UTGST Act, and the GST (Compensation to States) Act.
In order to ensure that the changes in the Centre and the State GST laws are brought into force simultaneously, these amendments are made effective from 01.02.2019.
MSME support and outreach program
With effect from 2nd
Further reforms in the current FY (2019-20):
New return system
Introduction of New Return System on a trial basis from 01.07.2019 and on a mandatory basis from 01.10.2019. SAHAJ & SUGAM Returns for small taxpayers are proposed
Single Cash Ledger
Rationalization of Cash Ledger in such a manner that earlier 20 heads are merged into 5 major heads. There is only one Cash Ledger for Tax, interest, penalty, fee & others.
Single Refund Disbursing: The Central or State Government which sanctions refund disburses all four major heads of refunds namely CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess.
Threshold limit for goods
A Threshold Limit of Rs 40 Lacs is offered to suppliers of goods as per the choice of States.
Composition Scheme for Services
Composition Scheme for small service providers up to an annual turnover of Rs 50 lacs with a tax rate of 6%
E-invoicing system
The electronic invoicing system in a phase-wise manner for B2B transactions is proposed to be introduced.
GSTAT
GST Appellate Tribunals are being established at various State Headquarters and area benches also.
Important Links to GST
Full-Form of GST
The term GST stands for Goods and Service Tax. It is a destination-based tax. Learn more about the meaning of GST and its features.
How to download a new GST certificate?
The newly registered taxpayer can download the GST certificate from the online portal. See the GST Certificate image and more.
Electronic invoice under gst
Learn about the new electronic invoicing under GST. Explore the notifications, FAQ, and E-invoicing dates.
GST Calculation in Excel
Download the GST calculation format in Excel. Reconcile the GST payment and input tax credit calculation.

